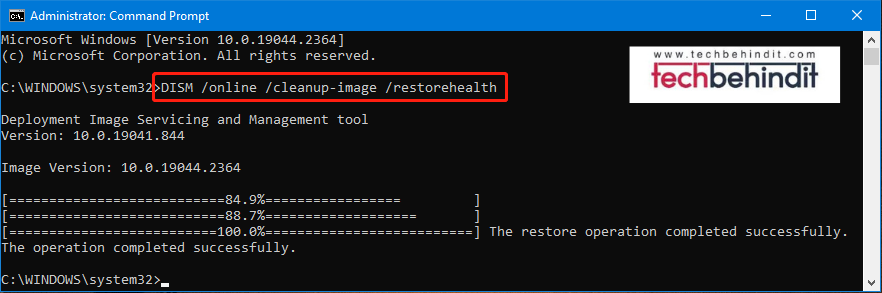
Dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth
- 1 The DISM Tool: What Is It?
- 2 Fixing Your Windows 10 or 11 Installation with DISM
- 3 The RestoreHealth Menu and Its Functions
- 4 How To Use The ScanHealth Function?
- 5 FAQs
- 5.1 What does DISM /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth do? T
- 5.2 When should I use DISM /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth?
- 5.3 Do I need administrative privileges to run this command?
- 5.4 Is an internet connection required to run this command?
- 5.5 How long does the DISM /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth process take?
- 5.6 Can I interrupt the process once it starts?
- 5.7 What should I do if the DISM /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth command doesn’t work?
- 5.8 Is there a log file I can check to see the results of the operation?
Damaged or corrupted system files are often at the root of Windows problems. When these essential files become corrupted or unreadable, Windows stops working as intended and displays a variety of error messages. Thankfully, Windows has a number of built-in tools that may be used to scan for problems, repair them, restore them, and troubleshoot them. The DISM instrument is one of these helpful instruments. The Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) programme is a powerful resource for Windows users experiencing issues ranging from slow performance to an inability to launch. You’ve likely heard of this tool on numerous how-to blogs, but are you familiar with its features? Do you understand the commands and their meanings? This manual will explain in depth what the DISM tool is, how to use it to rectify common mistakes, and what else it can do.
The DISM Tool: What Is It?
Network administrators can use Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) in Windows 10/11 to create, update, restore, and repair system images, including Windows Setup, Windows Recovery Environment, and Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE). The program can also be used to repair typical problems with the PC’s secret recovery image.
It’s a command-line programme for Windows that helps with image maintenance and creation. The Deployment Imaging Servicing and Management utility’s DISM.exe helps deploy the required images and poses no risk to your computer. Scan, repair, and replace damaged or missing system files using the locally accessible recovery image with the help of the System File Checker programme if your device is experiencing performance issues, does not boot up correctly, or you are troubleshooting errors.
The SFC programme won’t be able to fix Windows 10 or 11 if the replacement copies included in the recovery image are themselves corrupted. In this instance, the DISM tool must be used to check and fix the installation. To fix your installation, use SFC to access the Wim image where the new files are stored. The DISM tool is used to resolve issues that the SFC tool cannot. DISM issues commands to get your PC back into tip-top shape. These commands do not destroy anything, but they make substantial alterations to the system. Therefore, before performing these actions, you must ensure that you have a complete backup of your system.
Fixing Your Windows 10 or 11 Installation with DISM
The Deployment Image Service and Management Tool (DISM) is a powerful command-line tool in Windows 10 and 11 that can be used to repair the Windows installation, fix corrupted system files, and more. Here’s how to use DISM to fix your Windows 10 or 11 installation:
Note: Before you start, it’s a good idea to create a backup of your important data, or at least ensure that your data is backed up regularly, as these operations can impact your system.
- Open a Command Prompt with Administrative Privileges:
- For Windows 10:
- Press
Win + Xand select “Windows Terminal (Admin)” or “Command Prompt (Admin).”
- Press
- For Windows 11:
- Right-click the “Start” button and choose “Windows Terminal (Admin)” or “Command Prompt (Admin).”
- For Windows 10:
- Check and Repair the Image:You can use DISM to check and repair your Windows image. Here are some common commands:
- To check the health of your Windows image, run the following command:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth - To scan the image for corruption and attempt to repair it, use this command:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth
- If corruption is detected and you want to attempt a repair, use this command:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
- To check the health of your Windows image, run the following command:
- Use Source Files (Windows Installation Media):Sometimes, the repair process might require the original installation files from your Windows installation media. To specify the source files, you can add the
/Sourceparameter to theDISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealthcommand:DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:D:\Sources\Install.wim
Replace
D:\Sources\Install.wimwith the path to your Windows installation media. - Wait for the Process to Complete:The repair process may take some time, so be patient and allow it to finish. Once it’s done, you will receive a message indicating whether the operation was successful or if there were issues that couldn’t be resolved.
- Reboot Your System:After the repair process is completed, it’s a good practice to reboot your system to ensure that the changes take effect.
DISM is a powerful tool, and it can help resolve a variety of system issues. If you encounter any issues or are unsure about any steps, it’s advisable to seek professional assistance or contact Microsoft support for guidance.
Remember that DISM should be used with caution, and it’s always a good idea to have backups of your important data in case something goes wrong during the repair process.
Three different tasks can be accomplished with the help of the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) command tool:
- RestoreHealth
- CheckHealth
- ScanHealth
For DISM to function properly, you must execute these three parts in the specified order. Depending on the nature of the problem, you may need to perform more RestoreHealth settings in addition to these three.
The RestoreHealth Menu and Its Functions
If faults are found during the scan, you can have them fixed mechanically by running DISM with the RestoreHealth option.
These are the procedures to take to fix the image problem on Windows 10/11 using DISM:
- Do so by selecting the Play button.
- Try typing “command prompt” into the search field that appears next to the “Start” button.
- Click the first result, and then pick Run as administrator from the context menu.
- In order to fix problems, enter the following command into the command prompt window: Cleanup-Image RestoreHealth DISM Online
- Get in touch with the Enter key.
There will likely be a few pauses in the process, but that is to be expected. It will be finished in a few minutes if you just wait. The Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) programme will connect to the Windows Update servers and obtain the appropriate replacement files for any damaged Windows 10/11 local image once the processes have been finished.
The CheckHealth Menu and How to Use It
CheckHealth in DISM is a quick way to see if the local image has been damaged or corrupted, but it won’t fix the problem for you.
Follow these steps to scan the recovery image for errors using DISM:
- Do so by selecting the Play button.
- Try typing “command prompt” into the search field that appears next to the “Start” button.
- Click the first result, and then pick Run as administrator from the context menu.
- To perform a fast diagnostic, enter the following command into the command prompt window: Online DISM/Image Cleaning/Health Check
- Get in touch with the Enter key.
After everything is in place, the command will run to see if there is any data corruption that requires fixing.
How To Use The ScanHealth Function?
Running DISM with the ScanHealth option rather than CheckHealth will do a more thorough scan. Checking for issues in the Windows 10/11 image is the purpose of this.
Here’s how to use DISM’s sophisticated scanning features:
- Do so by selecting the Play button.
- Try typing “command prompt” into the search field that appears next to the “Start” button.
- Click the first result, and then pick Run as administrator from the context menu.
- To perform a thorough search, enter the following command into the appropriate command prompt: Online DISM/Image Cleaning/Health Checkup
- Get in touch with the Enter key.
After you’ve finished those, the more thorough scan will begin. The time it takes for the sophisticated scan to assess if the local image requires fixing is on the order of several minutes.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the Dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth command:
-
What does DISM /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth do? T
his command is used to scan the Windows image for corruption and attempt to repair it. It is often used when your Windows system files are corrupted, which can cause various issues like system instability or error messages.
-
When should I use DISM /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth?
You should use this command when you suspect that your Windows installation has corrupted system files. Common indications include system crashes, software not working correctly, or Windows Update errors.
-
Do I need administrative privileges to run this command?
Yes, you typically need administrative privileges (run as an administrator) to execute DISM commands because they involve system-level changes.
-
Is an internet connection required to run this command?
An internet connection may be required, as the DISM command may need to download replacement files from Windows Update to repair your system. It will prompt you to download files if needed.
-
How long does the DISM /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth process take?
The time it takes to complete this command varies depending on the system’s condition and the level of corruption. It can take several minutes to an hour or more in some cases.
-
Can I interrupt the process once it starts?
It’s generally recommended not to interrupt the process once it begins. Let it run to completion, as stopping it prematurely may leave your system in an unstable state.
-
What should I do if the DISM /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth command doesn’t work?
If the command fails to repair your system, you may need to use alternative methods, such as running sfc /scannow or considering a Windows repair or reinstallation.
-
Is there a log file I can check to see the results of the operation?
Yes, DISM creates a log file that can be found in %windir%\Logs\DISM\dism.log. You can review this log to see the details of what the command did.